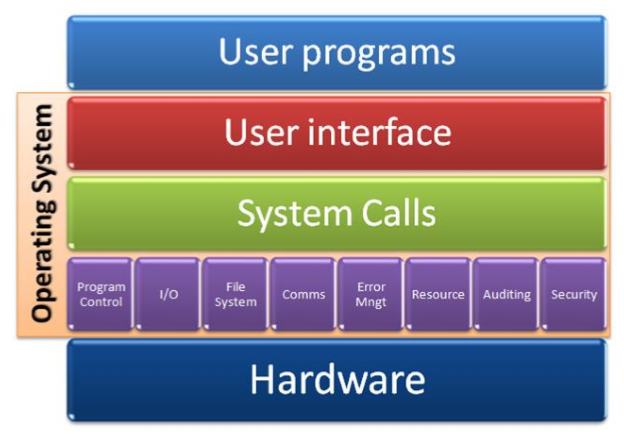
리눅스는 명령어가 너무 많다.
엑셀로 뽑아두고 하루종일 보고있으면 외워지기야 하겠지만, 제일 비효율적인 방법이라 생각한다.
어떤 단어의 줄임말인지 뇌리를 스쳐가도록 하기 위해, 약자를 다 달면서 설명해두겠다.
우선 명령어 체계의 기본적인 내용에 대해서 보자.
- 로그인

로그인 형식은 써보면 안다.
로그인에 쓰이는 데이터는, /etc/passwd에 저장이 된다.
login name : password : UID : GID : comment : home directory : shell program
- 파일 시스템
rwxㄱㅈㅌ를 기억하자. (그냥 기억하자.) 금방 설명할거다.

* 파일 이름은 \와 null을 써서는 안된다. (문자열의 형식 구분에 쓰이는 문자는 빼자는 것이다.)
* 14자 이하로 파일명의 길이를 제한하는 OS도 있다. 최대한 짧게 관리하자.
* . 이라는 파일은, 현재 디렉토리 경로를 뜻한다.
* .. 이라는 파일은, 상위 디렉토리 경로를 뜻한다.
ls라는 명령어는 list를 줄인 것으로서, 현재 디렉토리의 파일을 출력해준다.
뒤의 -al이라는 옵션은, 파일명 뿐만이 아닌 permission이나 파일 크기, 마지막 수정 날짜와 같은 구체적인 데이터도 표시해주는 옵션이다.
- Error handling
에러를 다루는 과정에 대해 알아보자.
에러가 발생했을 떄, 음수가 반환된다
errno라는 값이 어떤 에러가 발생했는지에 대해 더 자세히 살펴보기 위한 값을 제공해준다.
이는 <errno.h>라는 헤더파일에 정의되어있는데, 윈도우와 비교하여 무척 적으니 아래 목록에서 CTRL + F를 통해 검색하여 찾고, 참고하도록 하자.
{{
#define EPERM 1 /* Operation not permitted */
#define ENOENT 2 /* No such file or directory */
#define ESRCH 3 /* No such process */
#define EINTR 4 /* Interrupted system call */
#define EIO 5 /* I/O error */
#define ENXIO 6 /* No such device or address */
#define E2BIG 7 /* Arg list too long */
#define ENOEXEC 8 /* Exec format error */
#define EBADF 9 /* Bad file number */
#define ECHILD 10 /* No child processes */
#define EAGAIN 11 /* Try again */
#define ENOMEM 12 /* Out of memory */
#define EACCES 13 /* Permission denied */
#define EFAULT 14 /* Bad address */
#define ENOTBLK 15 /* Block device required */
#define EBUSY 16 /* Device or resource busy */
#define EEXIST 17 /* File exists */
#define EXDEV 18 /* Cross-device link */
#define ENODEV 19 /* No such device */
#define ENOTDIR 20 /* Not a directory */
#define EISDIR 21 /* Is a directory */
#define EINVAL 22 /* Invalid argument */
#define ENFILE 23 /* File table overflow */
#define EMFILE 24 /* Too many open files */
#define ENOTTY 25 /* Not a typewriter */
#define ETXTBSY 26 /* Text file busy */
#define EFBIG 27 /* File too large */
#define ENOSPC 28 /* No space left on device */
#define ESPIPE 29 /* Illegal seek */
#define EROFS 30 /* Read-only file system */
#define EMLINK 31 /* Too many links */
#define EPIPE 32 /* Broken pipe */
#define EDOM 33 /* Math argument out of domain of func */
#define ERANGE 34 /* Math result not representable */
#define EDEADLK 35 /* Resource deadlock would occur */
#define ENAMETOOLONG 36 /* File name too long */
#define ENOLCK 37 /* No record locks available */
#define ENOSYS 38 /* Function not implemented */
#define ENOTEMPTY 39 /* Directory not empty */
#define ELOOP 40 /* Too many symbolic links encountered */
#define EWOULDBLOCK EAGAIN /* Operation would block */
#define ENOMSG 42 /* No message of desired type */
#define EIDRM 43 /* Identifier removed */
#define ECHRNG 44 /* Channel number out of range */
#define EL2NSYNC 45 /* Level 2 not synchronized */
#define EL3HLT 46 /* Level 3 halted */
#define EL3RST 47 /* Level 3 reset */
#define ELNRNG 48 /* Link number out of range */
#define EUNATCH 49 /* Protocol driver not attached */
#define ENOCSI 50 /* No CSI structure available */
#define EL2HLT 51 /* Level 2 halted */
#define EBADE 52 /* Invalid exchange */
#define EBADR 53 /* Invalid request descriptor */
#define EXFULL 54 /* Exchange full */
#define ENOANO 55 /* No anode */
#define EBADRQC 56 /* Invalid request code */
#define EBADSLT 57 /* Invalid slot */
#define EDEADLOCK EDEADLK
#define EBFONT 59 /* Bad font file format */
#define ENOSTR 60 /* Device not a stream */
#define ENODATA 61 /* No data available */
#define ETIME 62 /* Timer expired */
#define ENOSR 63 /* Out of streams resources */
#define ENONET 64 /* Machine is not on the network */
#define ENOPKG 65 /* Package not installed */
#define EREMOTE 66 /* Object is remote */
#define ENOLINK 67 /* Link has been severed */
#define EADV 68 /* Advertise error */
#define ESRMNT 69 /* Srmount error */
#define ECOMM 70 /* Communication error on send */
#define EPROTO 71 /* Protocol error */
#define EMULTIHOP 72 /* Multihop attempted */
#define EDOTDOT 73 /* RFS specific error */
#define EBADMSG 74 /* Not a data message */
#define EOVERFLOW 75 /* Value too large for defined data type */
#define ENOTUNIQ 76 /* Name not unique on network */
#define EBADFD 77 /* File descriptor in bad state */
#define EREMCHG 78 /* Remote address changed */
#define ELIBACC 79 /* Can not access a needed shared library */
#define ELIBBAD 80 /* Accessing a corrupted shared library */
#define ELIBSCN 81 /* .lib section in a.out corrupted */
#define ELIBMAX 82 /* Attempting to link in too many shared libraries */
#define ELIBEXEC 83 /* Cannot exec a shared library directly */
#define EILSEQ 84 /* Illegal byte sequence */
#define ERESTART 85 /* Interrupted system call should be restarted */
#define ESTRPIPE 86 /* Streams pipe error */
#define EUSERS 87 /* Too many users */
#define ENOTSOCK 88 /* Socket operation on non-socket */
#define EDESTADDRREQ 89 /* Destination address required */
#define EMSGSIZE 90 /* Message too long */
#define EPROTOTYPE 91 /* Protocol wrong type for socket */
#define ENOPROTOOPT 92 /* Protocol not available */
#define EPROTONOSUPPORT 93 /* Protocol not supported */
#define ESOCKTNOSUPPORT 94 /* Socket type not supported */
#define EOPNOTSUPP 95 /* Operation not supported on transport endpoint */
#define EPFNOSUPPORT 96 /* Protocol family not supported */
#define EAFNOSUPPORT 97 /* Address family not supported by protocol */
#define EADDRINUSE 98 /* Address already in use */
#define EADDRNOTAVAIL 99 /* Cannot assign requested address */
#define ENETDOWN 100 /* Network is down */
#define ENETUNREACH 101 /* Network is unreachable */
#define ENETRESET 102 /* Network dropped connection because of reset */
#define ECONNABORTED 103 /* Software caused connection abort */
#define ECONNRESET 104 /* Connection reset by peer */
#define ENOBUFS 105 /* No buffer space available */
#define EISCONN 106 /* Transport endpoint is already connected */
#define ENOTCONN 107 /* Transport endpoint is not connected */
#define ESHUTDOWN 108 /* Cannot send after transport endpoint shutdown */
#define ETOOMANYREFS 109 /* Too many references: cannot splice */
#define ETIMEDOUT 110 /* Connection timed out */
#define ECONNREFUSED 111 /* Connection refused */
#define EHOSTDOWN 112 /* Host is down */
#define EHOSTUNREACH 113 /* No route to host */
#define EALREADY 114 /* Operation already in progress */
#define EINPROGRESS 115 /* Operation now in progress */
#define ESTALE 116 /* Stale NFS file handle */
#define EUCLEAN 117 /* Structure needs cleaning */
#define ENOTNAM 118 /* Not a XENIX named type file */
#define ENAVAIL 119 /* No XENIX semaphores available */
#define EISNAM 120 /* Is a named type file */
#define EREMOTEIO 121 /* Remote I/O error */
#define EDQUOT 122 /* Quota exceeded */
#define ENOMEDIUM 123 /* No medium found */
#define EMEDIUMTYPE 124 /* Wrong medium type */
#define ECANCELED 125 /* Operation Cancelled */
#define ENOKEY 126 /* Required key not available */
#define EKEYEXPIRED 127 /* Key has expired */
#define EKEYREVOKED 128 /* Key has been revoked */
#define EKEYREJECTED 129 /* Key was rejected by service */
}}}
위의 코드를 응용하는 방법이 있다.
echo $? 라는 명령어를 쉘에 입력해보자.
이전 실행된 명령어의 상태값을 확인할 수 있는데, 대부분 0(이상 없음)이 출력될 것이다.
0이 아닌 코드가 출력된다면, 위의 표에서 에러가 발생한 원인을 찾아보자.
- Signals
ps 라는 명령어가 있다.
process에서 따와, 현재 실행중인 프로세스를 모두 출력해준다.
이 때, 아래와 같은 형식으로 출력되는데,
PID : TTY : STAT : TIME : COMMAND
PID는 process를 identify 해주는 코드이다.
이 때 kill 명령어를 통해,

위와 같이
kill pid 형식으로 프로세스를 죽일 수 있다..!
-디렉터리
우선 리눅스에 적용되는 디렉토리 구조는 아래와 같다.

이 아래는 유닉스에 적용되는 디렉토리 구조는 아래와 같다.

내부적으로 조금 다른부분이 있다.
/boot 와 /kernel이 다르듯이.
하지만 우리는 리눅스를 공부한다.
/boot만 기억하자!
디렉터리 관련 명령어에서는 네가지 정도만 알아도 될 것 같다..!
- cd (change directory)
작업 디렉토리를 변경.
- pwd (print working directory)
현재 작업 디렉토리를 출력
- mkdir (make directory)
새 디렉토리를 생성
- ls (list)
디렉토리 내역을 출력한다.
옵션 !! 이 있다.
-s (all) -> 파일의 크기를 출력해준다.
-a (size) -> .과 ..파일을 포함해 숨은 파일도 다 출력해준다.
-l (long) -> 파일에 관련한 모든걸 출력해준다..!
옵션을 달 때는 - 뒤에 순서 상관없이 그냥 쭉 이어쓰면 된다..!
ex)

cat (catalog) 이라는 명령어도 있다.
*cat 뒤에 파일명을 그대로 붙이면 파일의 내용을 출력해준다.
*cat 뒤에 >, >>, <, <<를 붙여 추가적인 기능을 구현할 수 있는데, 이는 다시 이후에 설명하겠다.
cp (copy)
cp x1 x2
-> x1 파일의 복사본 x2를 만든다!
mv (move)
mv x1 x2
-> x1 파일의 이름을 x2로 교체한다!
rm (remove)
rm x1
-> x1파일을 삭제한다!
rm -r 디렉토리
-> 디렉토리 안의 모든 디렉토리, 파일을 제거한다.